Diabetes management involves a careful balance of diet, lifestyle, and medication. However, misinformation about what people with diabetes can or cannot eat can often lead to confusion and unnecessary dietary restrictions. Misleading food myths may cause anxiety and hinder the ability to make healthy choices. It's essential to separate fact from fiction to equip individuals with the correct information to manage their condition efficiently. Common misconceptions include the belief that all carbohydrates are harmful, or that people with diabetes need to avoid sugar entirely. These myths not only perpetuate misunderstandings about diabetes but can also impact the overall well-being of those living with the condition. By debunking these myths, individuals can gain a clearer understanding of their dietary options, promoting better health outcomes and a more varied and enjoyable diet.
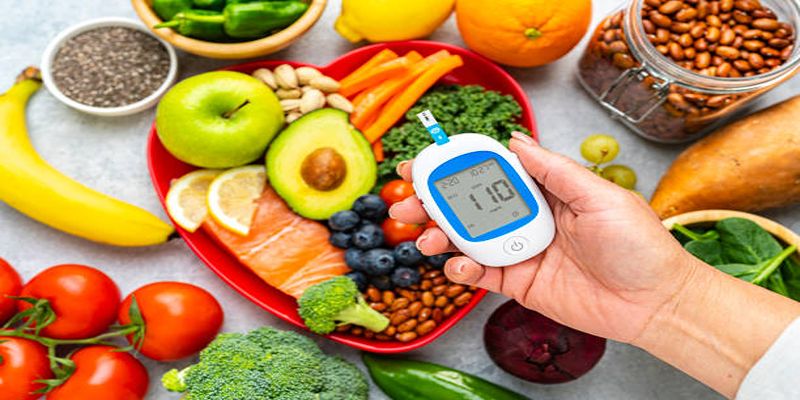

One of the most prevalent myths is that people with diabetes must completely eliminate carbohydrates from their diet. However, carbohydrates are an essential part of a balanced diet as they are a primary energy source for the body. The key is to choose the right types of carbohydrates and manage portion sizes effectively. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are nutritious sources that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, contributing to overall health.
Monitoring carbohydrate intake and pairing them with proteins or healthy fats can help maintain stable blood sugar levels without the need to forgo them entirely. Understanding how different carbohydrates affect the body enables individuals to enjoy a wider variety of foods within a diabetes-friendly diet plan.
Another common misconception is that people with diabetes must avoid sugar entirely. While managing sugar intake is crucial for maintaining stable blood glucose levels, it doesn't mean that all sugar is forbidden. Moderation is key, and sugar can be part of a balanced diet when consumed with awareness and care. It's important to consider the overall nutritional value of a meal and how it fits into one's daily dietary needs. Including small amounts of sugar in a meal plan can be possible, especially when it's balanced with other nutrients like fiber, healthy fats, and proteins.
By focusing on portion control and understanding the effects of sugar on the body, individuals with diabetes can incorporate their favorite treats occasionally without compromising their management goals.
Many people mistakenly believe that individuals with diabetes should avoid fruit due to its natural sugar content. However, fruit is packed with essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are beneficial for overall health. The key is to focus on portion sizes and the types of fruits consumed. Fruits with a lower glycemic index, such as berries, cherries, and apples, have a more gradual impact on blood sugar levels and can be included in a diabetes-friendly diet.
Additionally, consuming whole fruit, rather than fruit juices, provides fiber that aids in slowing the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Incorporating a variety of fruits in moderation allows individuals to enjoy the health benefits and natural sweetness that fruits offer without compromising their diabetes management.
There is a widespread belief that a high-protein diet is the best option for people with diabetes. However, while protein is an essential nutrient that helps build and repair tissues, an overemphasis on protein can sometimes lead to other health concerns. A diet disproportionately high in protein may strain the kidneys, especially in individuals with existing kidney issues, a common complication of diabetes. Instead of focusing solely on increasing protein intake, it's vital to maintain a balanced diet that includes appropriate amounts of carbohydrates and healthy fats.
Incorporating a variety of protein sources, such as lean meats, fish, beans, and legumes, can offer the necessary nutrients without overloading any one dietary component. Achieving a balanced intake ensures all nutritional needs are met, supporting overall health and effective diabetes management.
There is a common assumption that artificial sweeteners are a completely safe alternative to sugar for people with diabetes. While they can help reduce overall sugar intake and calorie consumption, not all artificial sweeteners are without concern. Some studies suggest that certain artificial sweeteners might affect gut health by altering the balance of gut bacteria, which can subsequently influence glucose metabolism. People with diabetes might also find that their taste preferences change with frequent use, potentially leading to an increased desire for sweet foods.
It's important to approach artificial sweeteners with caution and awareness, opting for natural alternatives like stevia or consuming them in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Consulting with healthcare professionals about the safe use of artificial sweeteners can further guide individuals in making informed choices that align with their diabetes management goals.

A pervasive myth suggests that people with diabetes should avoid snacking altogether. However, healthy snacking can actually be beneficial for managing diabetes. Eating smaller, balanced snacks between meals can help keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent overeating during main meals. The key is to choose snacks wisely, focusing on nutrient-dense options rather than processed, sugary foods. Healthy snack options include raw vegetables with hummus, unsweetened Greek yogurt with berries, or a handful of nuts.
By incorporating these kinds of snacks, individuals with diabetes can maintain energy levels throughout the day while still managing their blood sugar effectively. It's crucial to plan snacks as part of a comprehensive meal strategy to ensure they fit with one's overall dietary goals.
Challenging and debunking myths surrounding diabetes is crucial for promoting a more accurate understanding of the disease. By dispelling these misconceptions, individuals with diabetes can make informed choices that support their overall health and well-being. It's important to consult with healthcare professionals and registered dietitians to create a personalized meal plan that considers individual needs and preferences. With proper education and awareness, people with diabetes can enjoy a wide variety of foods while effectively managing their condition.

By Paula Miller/Oct 16, 2024

By Isabella Moss/Oct 15, 2024

By Madison Evans/Sep 20, 2024

By Georgia Vincent/Sep 27, 2024

By Madison Evans/Oct 15, 2024

By Maurice Oliver/Sep 20, 2024

By Juliana Daniel/Oct 16, 2024

By Maurice Oliver/Oct 15, 2024

By Alison Perry/Oct 15, 2024
By Sid Leonard/Oct 10, 2024

By Darnell Malan/Oct 31, 2024

By Jennifer Redmond/Oct 17, 2024